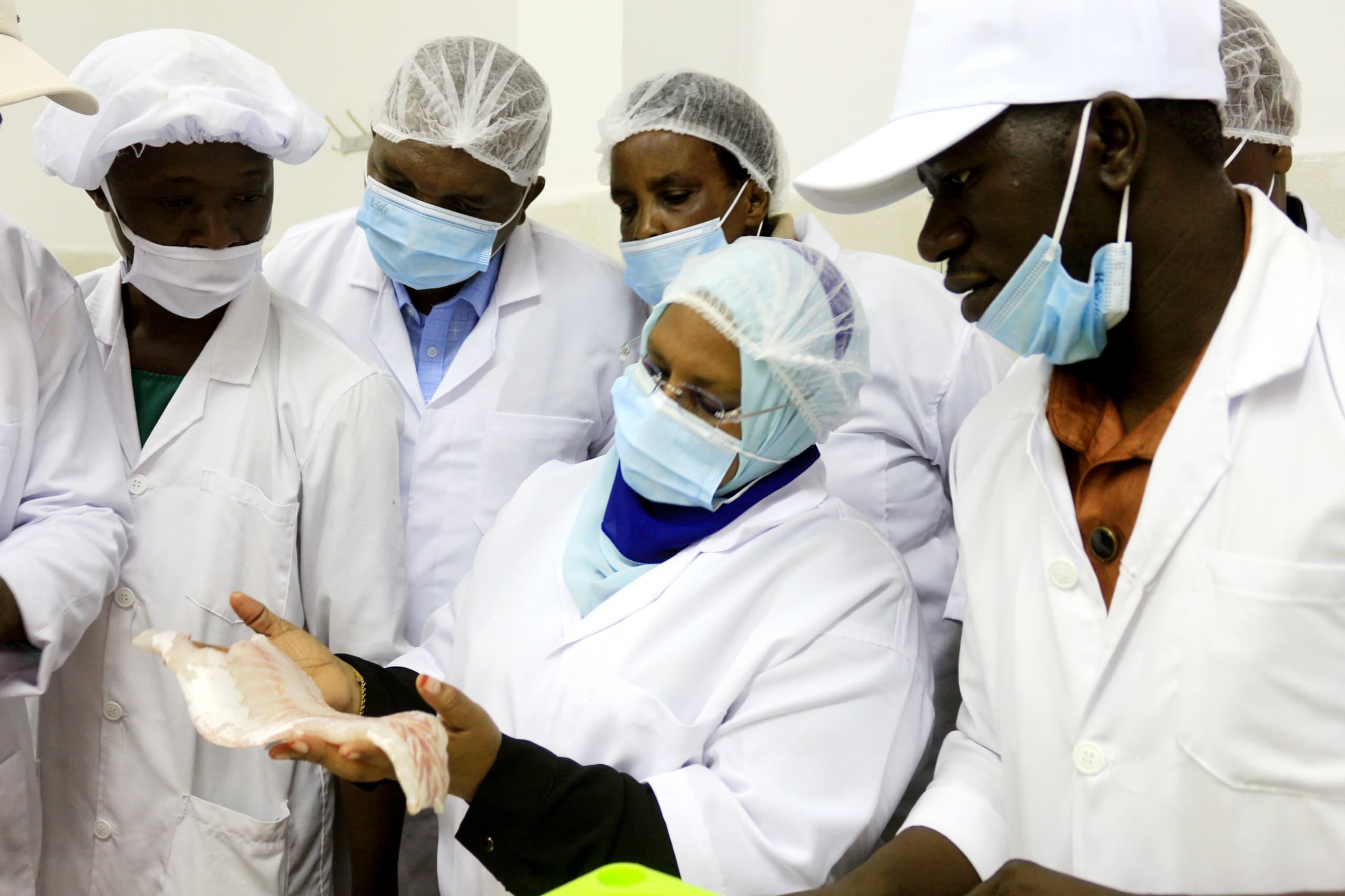
Exploration, partnerships necessary for influencing critical minerals investment

As the world demands more “new” minerals such as copper, lithium and rare earths for use in smart technologies for decarbonisation and clean energy production, African countries have some key considerations to take into account to garner investment in its rich endowment of these minerals.
In a panel hosted by Creamer Media on November 20, experts in the critical mineral sector and technology sphere discussed the importance of exploration and defining what critical minerals mean for the African continent.
Council for Geoscience CEO Mosa Mabuza said a critical minerals strategy must start with understanding each country’s mineral resources, how much more is left to uncover and what the country’s agenda with these minerals can be in the global supply chain.
The challenge, however, is underspending on exploration, with developed economies spending an average $65/m2 on geoscience and African countries only spending $5 /m2, yet Africa has always been a supplier of choice for minerals.
He suggested a deliberate continentwide approach to put together surveys of all African nations to find opportunities for collaboration and investing in more critical minerals discovery in an informed manner.
“A truly integrated value chain proposition can benefit the African continent and those that consume the minerals,” he said.
South Africa, for one, as a mature mining country has ample lessons to share that other countries can apply to their own mining sectors. “Our forebearers did a fantastic job of delineating mineral systems, particularly the Witwatersrand gold complex, the Bushveld Igneous Complex and the manganese fields in the Northern Cape.
“They consistently invested in geology to a certain point. There must be continuous research which will allow for some level of serendipitous discovery to happen,” Mabuza said, adding that South Africa has a solid foundation on which it is able to extrapolate when it moves into this new range of minerals that is creating a lot of enthusiasm.
He continued that key considerations for African countries now are what minerals the world will demand to reach net zero by 2050, what they have to offer and what policy will be best suited in this regard.
Zambia, for example, recently undertook a national air coverage geophysics survey totalling more than $100-million to acquire data. “Once you have taken a decision like that as a country, the rest can follow,” Mabuza said.
Industrial Development Corporation (IDC) senior industry specialist Kgashane Mohale advocated for more developmental institutions to consider financing for junior miners to conduct exploration, as the IDC itself is advancing an exploration fund together with government.
The corporation is finalising a first round of R160-million of grant funding to junior mining companies, as part of a R400-million total allocation, which the corporation will recover if projects are successful on a case-by-case basis through future ownership agreements.
For more these kinds of investments to release, Hyve Group’s Investing in African Mining Indaba content and strategic partnerships head Laura Nicholson said, naturally, countries’ regulations have a huge role to play in how critical minerals are developed.
Minerals Council South Africa CEO Mzila Mthenjane agreed, adding that more African countries need to start positioning the mining industry as a key catalyst for economic development, with the following decisions needing to be made in support of that view.
Top Headlines
© 2024 IPPMEDIA.COM. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED