Banks record strong growth of internet and mobile banking
Tanzania’s banking industry has recorded significant growth in internet and mobile banking services over the past five years, marking a major milestone in promoting a cashless economy and expanding financial inclusion.
The National Payment System Report 2023, recently published by the Bank of Tanzania (BoT), shows a rise in both internet and mobile banking transactions, with an increasing number of banks offering these services.
Commercial banks and financial institutions continue to develop innovative digital banking solutions, allowing customers to manage their finances conveniently through computers and mobile phones.
According to the report, the number of banks offering internet banking grew from 20 in 2019 to 35 in 2023. Similarly, mobile banking subscribers increased to 8.99 million from 5.04 million over the same period.
However, only 2.44 million of these mobile banking subscribers were active last year, highlighting the need for banks to continue promoting these services to boost adoption.
Despite the growth, digital fraud remains a significant challenge to the expansion of internet and mobile banking.
Many Tanzanians are still hesitant to use digital banking services due to concerns about security, which hampers efforts to promote a cashless economy.
In March 2024, the BoT reported that over 1.65bn/- ($647,000) was lost to mobile and internet banking fraud, including cyber-attacks, during the fourth quarter of last year. This was a sharp increase from the 901m/- ($353,600) lost in the previous quarter.
Mobile banking growth
Since its introduction in 2007, mobile money has filled the gap in accessing financial services caused by the complexities of traditional banking systems.
Between 2019 and 2023, mobile banking in Tanzania saw significant growth, driven by increased adoption of mobile money services and regulatory improvements aimed at enhancing financial inclusion.
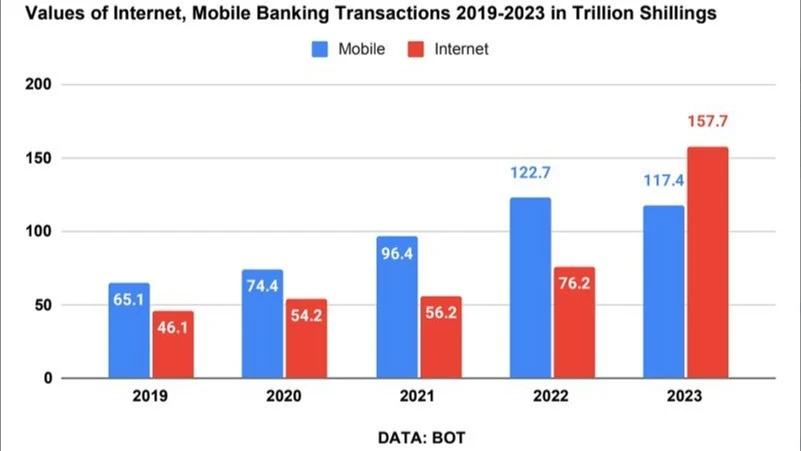
The report shows that the volume of mobile banking transactions increased from 55.74 million in 2019 to 81.99 million in 2023. The value of these transactions nearly tripled, rising from 9.47trn/- in 2019 to 25.51trn/- last year.
The COVID-19 pandemic also accelerated the adoption of mobile banking, as people sought contactless payment options.
The BoT encouraged mobile money usage by waiving certain transaction fees and raising transaction limits, leading to a surge in transaction volumes during the pandemic.
By 2023, mobile banking had reached more remote areas of Tanzania, contributing significantly to financial inclusion.
The expansion of 4G networks by mobile operators, along with the increasing affordability of smartphones and mobile data packages, further boosted mobile banking usage.
Internet banking expansion
The National Payment System Report 2023 also highlights the growth of internet banking in Tanzania. The number of registered internet banking customers rose from 217,425 in 2017 to 313,585 in 2023, while active customers increased from 31,706 in 2019 to 134,091 last year.
Annual customer growth ranged between 12 percent and 32 percent over the past five years, except in 2021 when growth declined by 29.37 percent due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The volume of domestic internet banking transactions grew from 5.2 million in 2019 to 16.1 million in 2023. International transactions also surged from 20,201 to 1.5 million during the same period.
The value of domestic transactions increased from 43.2trn/- in 2019 to 142.6trn/- in 2023, while international transaction values rose from 2.9trn/- to 15.2trn/-.
As internet penetration continues to expand, more Tanzanians are adopting internet banking services. The number of internet users in the country has risen significantly, driven by infrastructure development and lower data costs.
However, internet banking remains more popular in urban areas where internet infrastructure and computer ownership are more common. In contrast, rural areas continue to rely heavily on mobile banking services.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, internet banking usage surged as customers sought to minimize physical contact and manage their finances remotely.
Banks promoted the use of digital platforms, with some waiving fees for online transactions to encourage adoption.
As internet banking continues to grow, cybersecurity has become a critical focus for banks. Investments in enhanced security measures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and encrypted communications, are aimed at preventing fraud and cyberattacks.
Banks are also undertaking campaigns to educate customers about the benefits of internet banking, including tutorials on how to use online platforms, protect personal data, and manage finances digitally.
However, challenges remain, particularly in rural areas where internet infrastructure is less reliable.
Slow internet speeds and intermittent connectivity issues limit access to internet banking for some users.
While internet banking has expanded, it still faces competition from mobile banking platforms, which are more widely used for everyday transactions due to their simplicity and broader reach, especially in areas with limited access to computers and stable internet connections.
Top Headlines
© 2025 IPPMEDIA.COM. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED